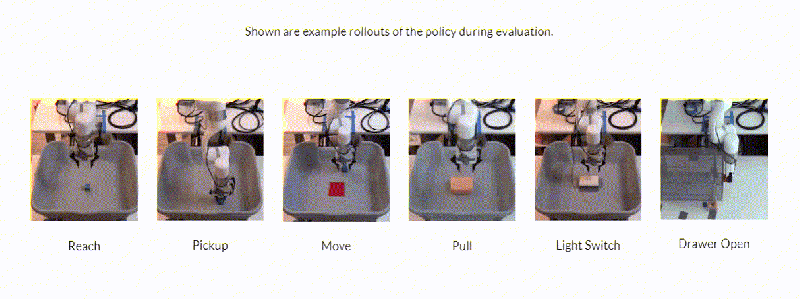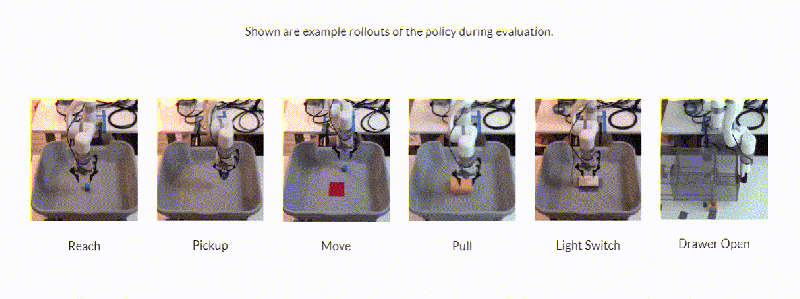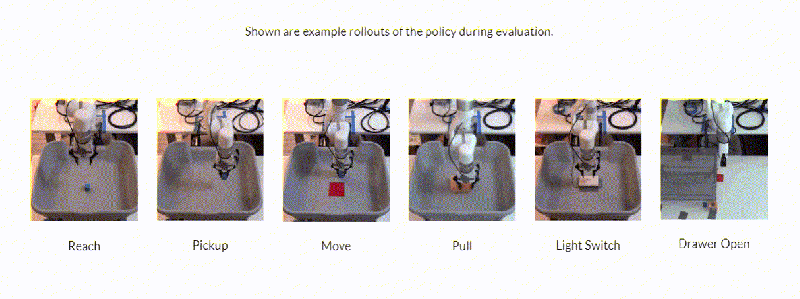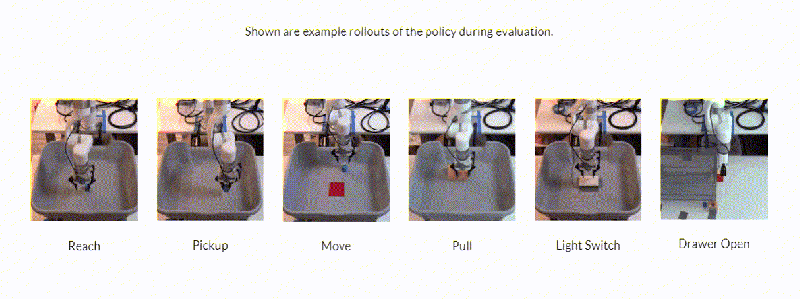
Stimulated on by this, researchers on the College of California, Berkely developed a framework– Framework for Environment friendly Robotic Manipulation (FERM)– that leverages innovative techniques to achieve what they state is “extremely” sample-efficient robotic control algorithm training. The coauthors say that, provided solely 10 presentation amounting to fifteen to 50 minutes of real-world coaching time, a single robotic arm can be taught to be successful in, decide, move, and pull huge objects or flip a modification and open a drawer utilizing FERM.
McKinsey pegs the robotics automation potential for manufacturing occupations at round 80%, and the pandemic is most likely to accelerate this shift. A report by the Manufacturing Institute and Deloitte discovered that 4.6 million production jobs will need to be packed over the subsequent years, and difficulties introduced on by physical distancing measures and a continual uptick in ecommerce exercise have actually extended some logistics operations to the limit. The Nationwide Affiliation of Producers states 53.1% of manufacturers expect a change in operations as a result of well being disaster, with 35.5% stating theyre already handling offer chain disruptions.
FERM may help accelerate the shift towards automation by making “pixel-based” support studying– a type of machine studying through which algorithms be taught to end up tasks from taped demonstrations– extra data-efficient. Due to the fact that the researchers clarify in a paper, FERM first collects a little variety of stores and demonstrations them in a “replay buffer.” An encoder maker studying algorithm pretrains on the demonstration understanding contained throughout the replay buffer. Then, a reinforcement studying algorithm in FERM trains on photos “augmented” with knowledge produced each by the encoder and the initial presentations.
In action to the researchers, FERM is straightforward to put together because it entirely needs a robotic, a graphics card, two cameras, a handful of demonstrations, and a benefit operate that guides the reinforcement studying algorithm towards a function. In experiments, they are saying that FERM made it possible for an xArm to be taught six responsibilities inside 25 minutes of coaching time (corresponding to twenty to 80 episodes of training) with a typical success charge of 96.7%. The arm might even generalize to things not seen throughout coaching or presentations and deal with barriers blocking its choice to purpose positions.
Spurred on by this, researchers on the College of California, Berkely established a structure– Framework for Environment friendly Robotic Manipulation (FERM)– that leverages advanced methods to achieve what they state is “extremely” sample-efficient robotic manipulation algorithm coaching. The coauthors state that, provided solely 10 presentation amounting to fifteen to 50 minutes of real-world coaching time, a single robotic arm can be taught to succeed in, choose, transfer, and pull giant things or flip a change and open a drawer making use of FERM.
In reaction to the scientists, FERM is simple to put together in that it entirely requires a robotic, a graphics card, two cams, a handful of presentations, and a benefit run that guides the reinforcement studying algorithm towards a purpose. Open supply frameworks like FERM assure to advance the advanced in robotic control, however there stay questions on how to measure development.
” To the ideal of our details, FERM is the primary method to unravel a various set of sparse-reward robotic adjustment responsibilities immediately from pixels in lower than one hour,” the scientists wrote. “Because of the restricted quantity of guidance required, our work provides exhilarating opportunities for using reinforcement studying to real robots in a quick and environment friendly method.”
Open supply frameworks like FERM guarantee to advance the cutting edge in robotic manipulation, however there stay concerns on how to measure progress. As my colleague Khari Johnson composes, metrics used to determine development in robotic greedy can vary primarily based on the responsibility. For robotics working in a mission-critical setting like area, accuracy concerns above all.
” Below sure circumstances, if weve got good objects and youve got a truly quick robotic, you might arrive [human picking rates],” roboticist Ken Goldberg informed VentureBeat in a earlier interview. “However they are stating people resemble 650 per hour; thats a significant phase. Its very burdensome to beat individuals. Were excellent. Weve advanced over thousands and countless years.”






